Ore and engineering geophysics
The methods used:
• intelligence, magnetization;
• electric exploration of various modifications;
• radiometry;
• geophysical well logging;
• gas shooting.
The tasks solved:
• preparation of geophysical foundations to study geological structure of the territory and search for deposits of gold, diamonds, ores and non-metallic minerals;
• prediction of mineral deposits on the basis of automated forecasting systems (AFS);
• study of hydrogeological conditions of solid mineral deposits;
• search for drinking groundwater with determination of well location, their drilling and arrangement;
• determination of groundwater level;
• forecast of the groundwater regime;
• study of groundwater dynamics;
• study of groundwater mineralization and temperature;
• study of aeration zone;
• forecast and study of water-logging areas, including urban agglomerations;
• creation and maintenance of water drainage systems in water-logging areas;
• forecast and study of landslide processes and engineering protection from them;
• forecast and study of karst processes;
• study of technogenic pollution of the environment;
• radio-ecological monitoring of soils and surface waters;
• radiation control in the construction;
• engineering and geophysical research in the construction of ground and underground structures;
• monitoring of the state of hydrotechnical structures (dams, tailing facilities, etc.);
• study of corrosion of pipelines;
• study of dynamic state of the rocks in which pipelines are located.
During regional surveys, based on geophysical works (gravity survey, magnetizing, electrical exploration), the geophysical bases for geological studies of areas of various scales are being prepared. According to the results of works, models of the studied areas are created. The maps of complex interpretation of geological and geophysical materials for the sedimentary cover and the foundation which are used for the construction of geological maps as well as the maps of forecast of prospective areas for the search for minerals are also created.
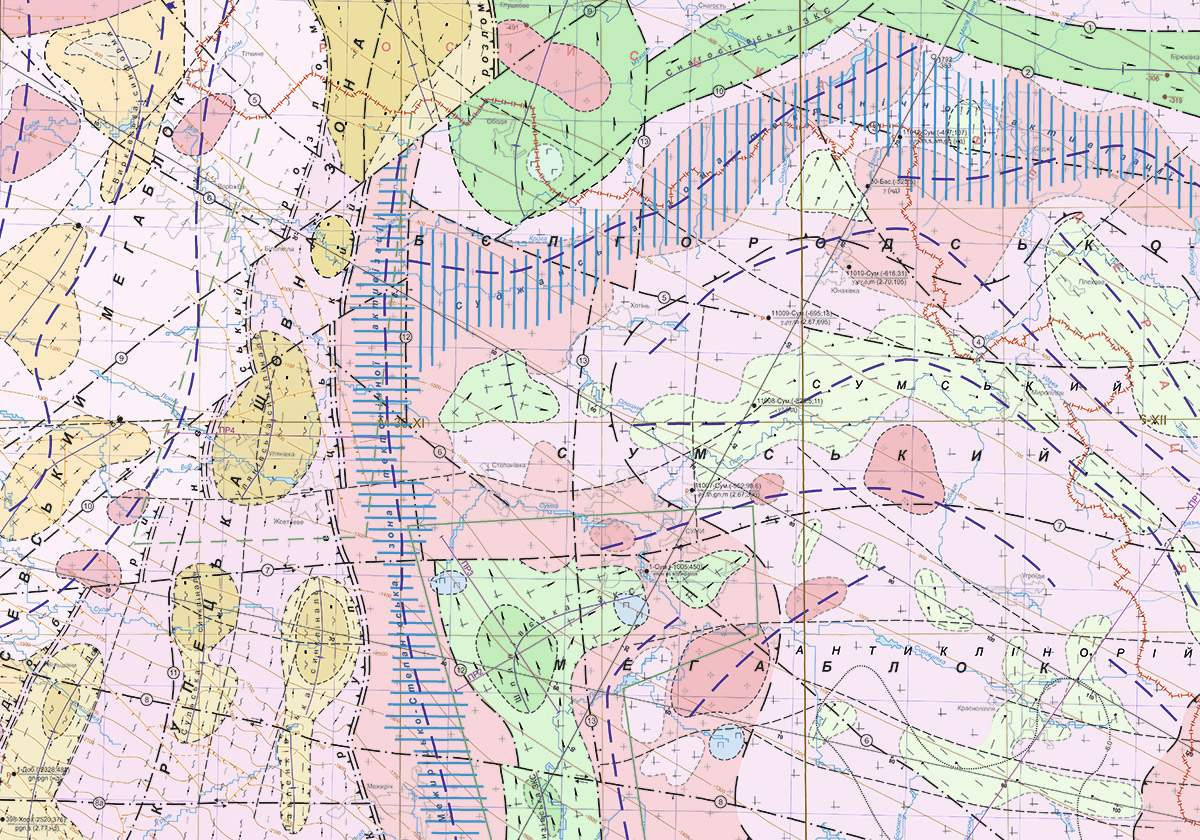
An example of the map of complex interpretation of geological and geophysical materials for Precambrian formations when creating a geophysical basis is depicted in Fig. 1.
Fig.1 Map of complex interpretation of geological and geophysical materials for Precambrian formations
One of the variants of the model based on the results of the modeling of the gravitational field is shown in Fig. 2
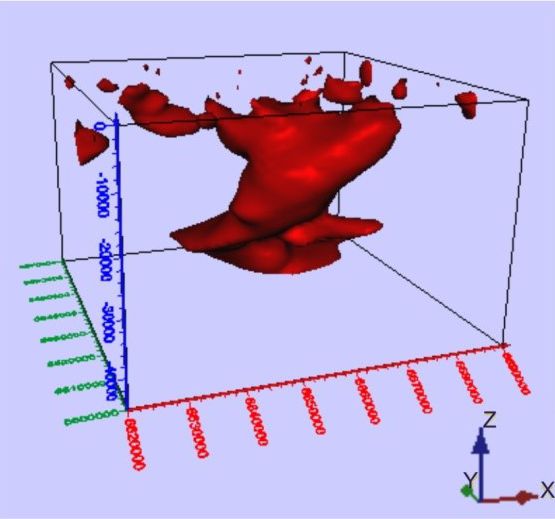
Fig.2 Three-dimensional model of gravitational masses of Krasnopolye gravitational maximum (view from the north)
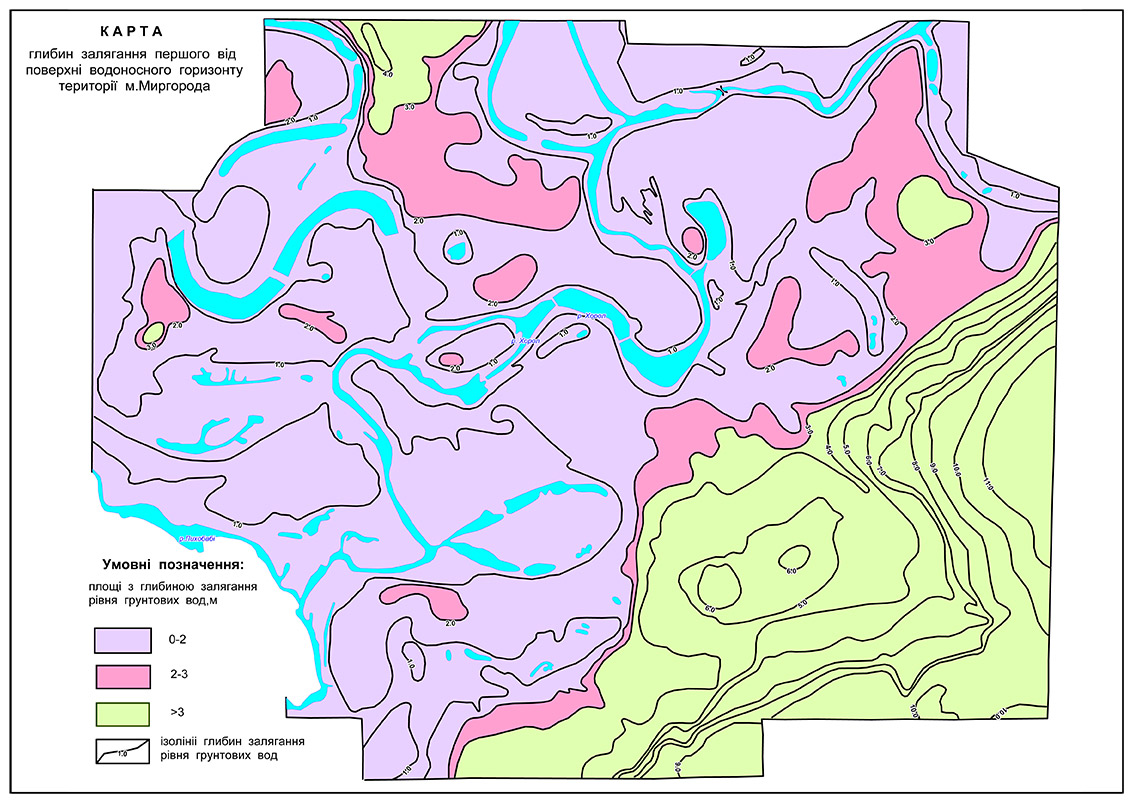
It is effective to use geophysical methods in the study of exogenous geological processes (EGP) – water-logging, landslides, karst, etc. The most progressive exogenous process that causes significant damage to the state is water-logging. The map of depths of the aquifer being the first from the surface of Mirgorod created on the results of geophysical studies is shown in Fig. 3.
Fig. 3 Map of depths of the aquifer being first from the surface of Mirgorod
An example of application of geophysical methods in the study of karst and collapse processes in the Kryvbas region is shown in Fig.4.

Fig. 4 Results of 2D inversion of the magnetotelluric field. Available craters are shown in blue